Our Services
Shalom Orthopaedic Hospital is fully equipped with the appropriate emergency medical service facilities & equipment in the accident and emergency department to help the victims of accidents & critical patients.
The most common types of accidents involve automobile and road accidents, sports-related accidents, fall injuries, or fire accidents. It is important to understand the emergency services and emergency management required during an accident for the victim.
The critical care of victims who have suffered injuries during the accident (e.g. roadside accident) or suffered from life-threatening conditions like brain stroke, heart attack or septic shock, etc. is handled by the Accident & Emergency (A&E) department of the hospital. Paramedics who work in the A&E department provide the accident victims with emergency medical services, ambulance services and provide transport to the emergency room.
The Department of Physiotherapy at Shalom Orthopaedic Hospital offers specialized care to its patients using the latest treatment procedures of international standards in a very friendly and personalized manner. It has one of the largest and well-equipped computerized modalities. The physiotherapy center offers a multifaceted approach for the patient’s rehabilitation by a well-qualified and highly experienced team of physiotherapists. Our team of physiotherapists is highly trained and works closely with a Medical Specialist to help patients to maximize their quality of life before and after surgery and also during conservative treatment.
We at Shalom Orthopaedic Hospital formulate and plan treatments and exercises that help relieve pain for better mobility and balance. We also guide and help in the prevention of surgery, manage degenerative changes and avoid dependency on medicines. We diagnose the condition and the main cause behind it. We plan and carry out a series of treatments to help patients to go back to living a long and healthy life without any pain and discomfort.

Fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). A fracture often requires emergency treatment at a hospital. Before transporting the person, protect the injured area to avoid further damage. For broken arm or leg bones, put a splint (made of wood, plastic, metal, or another rigid material padded with gauze) against the area to prevent movement; loosely wrap the splint to the area using gauze.
If there is bleeding, apply pressure to stop bleeding before splinting, then elevate the fracture. Fractured bones must be set in their proper place and held there in order to heal properly. Setting a bone is called "reduction."
Repositioning bone without surgery is "closed reduction." Most fractures in children are treated with closed reduction. Serious fractures may require open reduction -- repositioning using surgery. In some cases, devices such as pins, plates, screws, rods, or glue are used to hold the fracture in place. Open fractures must also be cleaned thoroughly to avoid infection.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis (a condition that affects your joints). Healthcare providers sometimes refer to it as degenerative joint disease or OA. It happens when the cartilage that lines your joints is worn down over time and your bones rub against each other when you use your affected joints.
Usually, the ends of bones in your joints are capped in a layer of tough, smooth cartilage. Cartilage is like a two-in-one shock absorber and lubricant — it helps the bones in your joints move past each other smoothly and safely. If you have osteoarthritis, the cartilage in your affected joints wears away over time. Eventually, your bones rub against each other when you move your joints.
Osteoarthritis can affect any of your joints, but most commonly develops in your
- Hands
- Knees
- Hips
- Neck (cervical spine)
- Lower back (lumbar spine)
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the joint through a small incision. Arthroscopic procedures can be performed to evaluate or treat many orthopaedic conditions including torn cartilage (known by health professionals as "meniscus"), torn surface (articular) cartilage, ACL reconstruction, and trimming damaged cartilage.
A pediatric orthopaedist is the best-trained and most experienced doctor to properly evaluate and treat musculoskeletal (bone, joint, or muscle) problems in a child who is still growing. This includes newborn babies through teenagers. Pediatric orthopaedic surgeons choose to make the care of children the focus of their medical practice. The unique nature of medical and surgical care of children is learned from advanced training and experience in practice.

Back pain is a common reason people consult their doctor, and in many cases, conservative treatment, including physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications, can bring relief. However, spinal deformity, spinal infections, trauma, spine tumors and some degenerative spine conditions, such as stenosis and herniated disks, may require surgical treatment. For the best outcome, it makes sense to consult a spine surgery team with plenty of experience.
The spine surgeon may opt for an open (traditional) spine surgery procedure, which involves an incision along the backbone. The surgeon moves muscle and soft tissue aside to gain access to the bones of the spine and the spinal cord. Minimally invasive techniques involve a smaller incision and the insertion of a tube, through which the surgeon inserts small surgical instruments to work on the spine. Minimally invasive techniques may be able to shorten recovery time and reduce the risk of complications.
Robotic spine surgery procedures can use GPS-like tracking systems to assist the spine surgeon in extremely precise placement of screws and other hardware in the course of repairing a damaged or deformed spine.

Plastic surgery takes its name from the Greek word “plastikos,” which means to “form” or “mold.” It includes a group of procedures that alter certain areas of your body. These include your face, neck, breasts, stomach, arms and legs. The terms “reconstructive plastic surgery” and “cosmetic surgery” may seem similar, but they represent different types of procedures. Reconstructive surgery repairs defects or injuries from trauma. It also restores function and a natural-looking appearance.
You may need this type of surgery if you have:
- Birth defects, such as webbed fingers, cleft lip and palate.
- Burns.
- Certain medical conditions, like head and neck cancer or breast cancer.
- Scars that prevent natural movement.
- Severe injuries, like cuts or tears over large areas of skin.
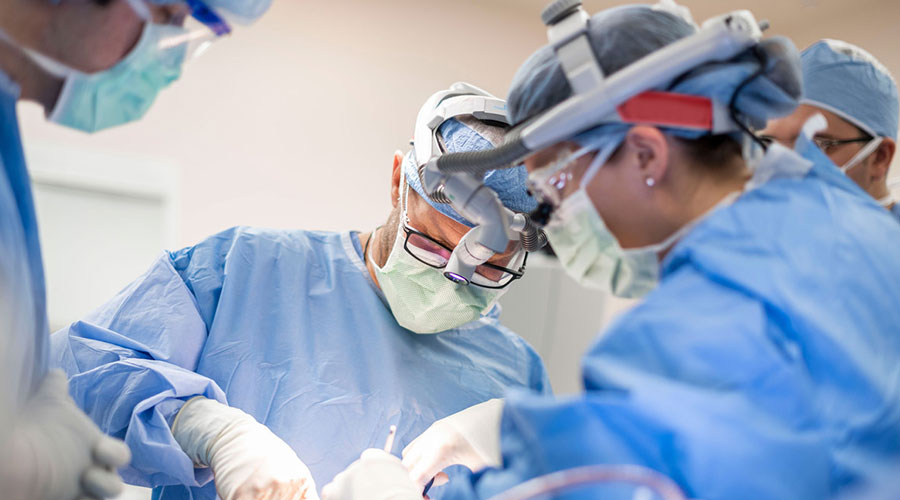
Limb lengthening and reconstruction techniques can be used to replace missing bone and lengthen and/or straighten deformed bone segments. The procedures may be performed on both children and adults who have limb length discrepancies, or limb deformities such as bow legs or knock knees, due to birth defects, diseases or injuries. The limb lengthening and limb deformity correction process works on the principle of distraction osteogenesis. This is a revolutionary concept that reverses the long-held belief that bone cannot be regenerated.
In this process, a bone that has been cut during surgery can be gradually distracted (pulled apart), leading to new bone formation (osteogenesis) at the site of the lengthening. In this way, bone segments can be lengthened by 15 to 100 percent of their original length. We use a variety of techniques, including the use of monolateral (one-sided) and circular external fixation devices, to correct angular deformities as well as limb length discrepancies.
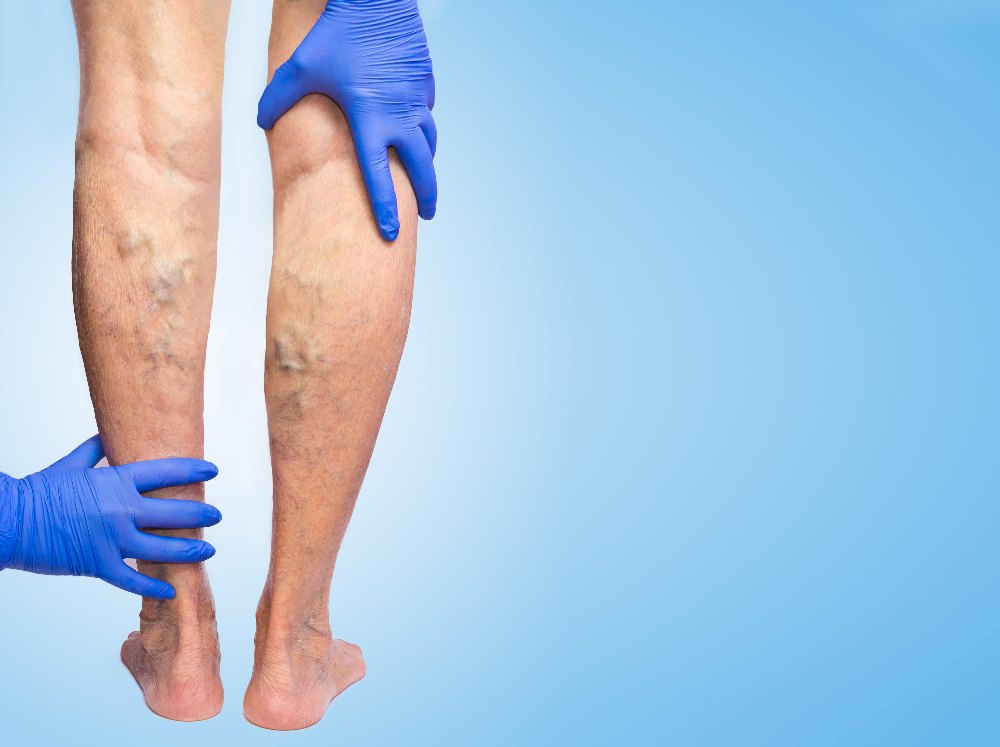
Reconstructive surgery is primarily performed to rebalance the hand for useful function. It can also often improve the appearance of the hand cosmetically, and in doing so, improve the patient's self-image.
The real reason for reconstructive surgery is to rebalance the hand and fingers in order that they work in normal positions that allow the hand to be used satisfactorily. Post-operative rehabilitation is needed in order to make the surgery successful and maximize the result. Hand therapists have developed specialized techniques for the restoration of hand function that maximize the effectiveness of reconstructive surgery.
- Hand therapy
- Surgical rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is care that can help you get back, keep, or improve abilities that you need for daily life. These abilities may be physical, mental, and/or cognitive (thinking and learning). You may have lost them because of a disease or injury, or as a side effect from a medical treatment. Rehabilitation can improve your daily life and functioning.
Who needs rehabilitation?
Rehabilitation is for people who have lost abilities that they need for daily life. Some of the most common causes include:
- Injuries and trauma, including burns, fractures (broken bones), traumatic brain injury, and spinal cord injuries
- Stroke
- Severe infections
- Major surgery
- Side effects from medical treatments, such as from cancer treatments
- Certain birth defects and genetic disorders
- Developmental disabilities
- Chronic pain, including back and neck pain




 Emergency Contact
Emergency Contact Ambulance Service
Ambulance Service